In today’s digital age, where technology often dominates our interactions, the power of emotional design cannot be underestimated. Emotional design focuses on creating experiences that evoke positive emotions, forge human connections, and leave a lasting impact on users. By understanding the psychological and emotional aspects of design, businesses can create products and services that resonate deeply with their audience. In this article, we will explore the concept of emotional design and its significance in fostering human connection and driving engagement.
I. Understanding Emotional Design
Emotional design refers to the intentional creation of design experiences that evoke emotional responses in users. It goes beyond aesthetics and focuses on tapping into users’ emotions to create meaningful and memorable experiences. The core principles of emotional design include the three levels of emotional design: visceral, behavioral, and reflective.
Visceral Design: This level of emotional design targets immediate, instinctive reactions and relies on sensory stimuli. It aims to elicit initial emotional responses based on visual aesthetics, colors, shapes, and other sensory elements.

Behavioral Design: This level focuses on the usability and functionality of the design, considering how it facilitates users’ goals and tasks. It aims to create positive emotional responses by providing an efficient and enjoyable user experience.
Reflective Design: This level involves the user’s contemplation and reflection after using the design. It aims to create a deeper emotional connection by aligning with users’ values, aspirations, and personal narratives.
II. The Psychology of Emotional Design
Emotional design is influenced by various psychological factors that impact human emotions. These factors include:
Color: Different colors can evoke specific emotional responses. Warm colors like red and orange can convey energy and excitement, while cool colors like blue and green can evoke calmness and tranquility.
Typography: Typography choices, such as font styles and sizes, can influence emotional responses. For example, serif fonts may convey tradition and reliability, while handwritten fonts can evoke a personal and friendly feel.
Imagery: Images and visuals play a crucial role in emotional design. The choice of imagery, including photographs, illustrations, or icons, can evoke specific emotions and create a connection with users.
User Interactions: Interactions and animations can enhance emotional engagement. Microinteractions, such as subtle transitions or playful feedback, can create moments of delight and surprise for users.
III. Designing for Empathy and Connection
Empathy is a crucial element in emotional design. Designers need to understand and connect with users’ needs, emotions, and motivations to create designs that resonate. By putting themselves in users’ shoes, designers can develop a deep understanding of their experiences and design accordingly.
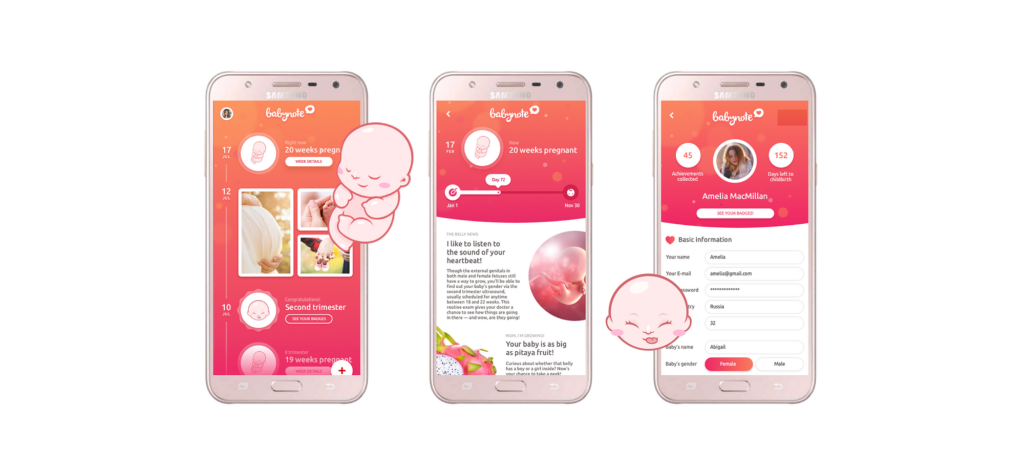
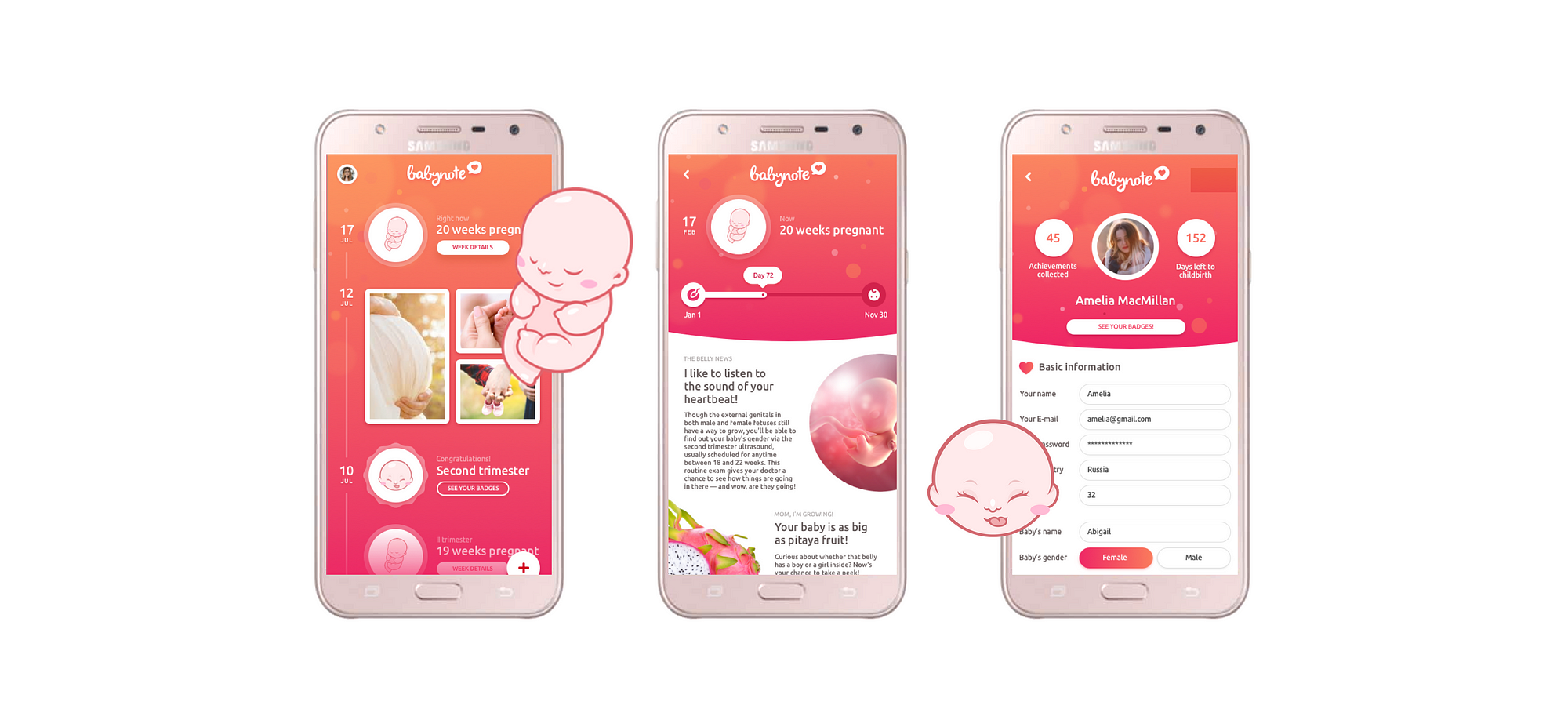
Storytelling and narrative are effective tools for establishing an emotional connection. By creating relatable experiences and narratives, designers can evoke empathy and forge a meaningful connection between the user and the design.
IV. Elements of Emotional Design
Visual Aesthetics: The overall visual appeal, including layout, composition, and graphic elements, can evoke specific emotions and shape the user’s perception of the design.
Microinteractions: Small, subtle animations and interactive elements can create delightful moments and evoke positive emotional responses, fostering a sense of engagement and enjoyment.
Sound: Sound and audio elements can enhance emotional design by creating atmosphere, evoking specific moods, or providing auditory feedback to user interactions.

Haptic Feedback: Tactile feedback, such as vibrations or haptic responses, can enhance the emotional connection by providing a tangible and immersive experience.
Personalization and customization also play a significant role in emotional design. Allowing users to personalize and customize their experiences creates a sense of ownership and emotional attachment to the design.
V. Case Studies: Successful Examples of Emotional Design
Several brands and products have successfully implemented emotional design strategies to connect with users. For example, Apple’s design philosophy focuses on creating products that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also evoke a sense of joy and delight through intuitive interactions.
Companies like Airbnb and Nike have effectively used emotional design to create meaningful and memorable experiences for their users. Airbnb’s design encourages users to feel at home and connect with local cultures, while Nike’s design promotes motivation and personal achievement.
VI. Designing Ethically and Responsibly
In emotional design, ethical considerations are essential to ensure that users’ emotions are not manipulated or exploited. Designers should strive for transparency and honesty, avoiding deceptive practices that may compromise users’ trust.
Designing for inclusivity, diversity, and cultural sensitivity is crucial. Emotional design should consider the diverse backgrounds, needs, and perspectives of users to avoid excluding or marginalizing any particular group.
By considering ethical principles and designing with inclusivity in mind, emotional design can create positive and meaningful experiences that resonate with users on a deeper level.
In conclusion, emotional design has the power to create memorable experiences, forge strong connections, and drive meaningful engagement with users. By understanding the psychological and emotional aspects of design, businesses can create products, services, and digital experiences that resonate deeply with their audience. Incorporating emotional design principles into the design process allows brands to stand out in a crowded marketplace and build lasting relationships with their customers.
Key Takeaways:
- Emotional design taps into users’ emotions, creating meaningful and memorable experiences.
- Understanding the psychology of design elements helps evoke desired emotional responses.
- Empathy and storytelling are key in establishing a deep emotional connection with users.
- Elements such as aesthetics, microinteractions, and personalization contribute to emotional design.
- Designing ethically and responsibly ensures a positive impact on users and society.
Harness the power of emotional design to create experiences that connect with your audience on a deeper level. Contact us today to discuss how our team can help you integrate emotional design principles into your branding and user experience strategies.
Leave a Reply