When it comes to building a strong brand identity, logo design takes center stage. A logo serves as the visual representation of a brand, encapsulating its essence, values, and personality. As the face of a brand, a well-designed logo has the power to captivate and engage audiences, leaving a lasting imprint in their minds. However, creating an effective logo is no easy task. It requires a deep understanding of the brand, its target audience, and the principles of design.
In this article, we will explore the dos and don’ts of logo design, providing valuable insights and guidelines to help you craft a logo that not only captures the essence of your brand but also resonates with your audience. Join us as we embark on a journey into the realm of logo design and discover the key principles and pitfalls to avoid, ensuring that your logo stands the test of time and represents your brand with excellence.
I. Validating Design Concepts:
Validating design concepts is a crucial step in the design process to ensure that the final product meets user needs and expectations. There are several methods and approaches to validate design concepts effectively.
User Feedback: Prototyping enables designers to gather feedback directly from users, allowing them to understand user preferences, pain points, and expectations early in the design process. By presenting a prototype to users and observing their interactions and feedback, designers can gain valuable insights into how users perceive and interact with the design. This feedback helps in making informed design decisions and avoiding costly mistakes down the line.
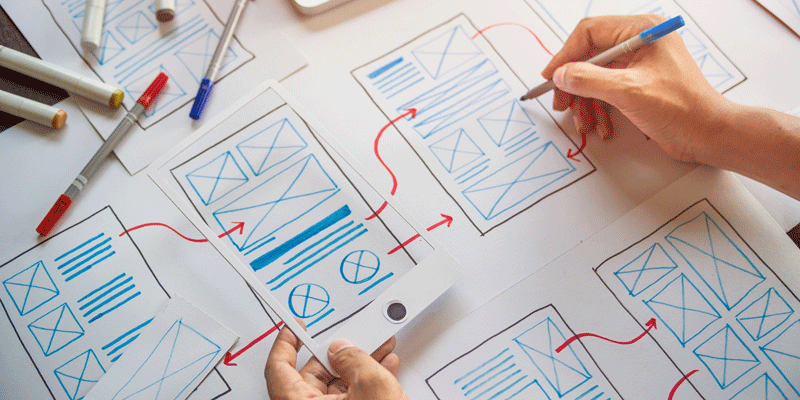
Iterative Design: Prototyping facilitates an iterative design approach, where designers can quickly test and refine multiple design concepts. By creating multiple prototypes, designers can explore different solutions, evaluate their effectiveness, and iterate on their designs based on user feedback. This iterative process helps refine the design and ensure that it aligns with user needs and expectations.
II. Enhancing User Experience:
User Testing: Prototyping allows designers to conduct user testing sessions, where real users interact with the prototype and provide valuable insights. User testing helps identify usability issues, understand user behavior, and make improvements to enhance the overall user experience. Through user testing, designers can observe how users navigate through the prototype, identify points of confusion or frustration, and gather suggestions for improvement. This feedback helps refine the design and create a more intuitive and user-friendly experience.
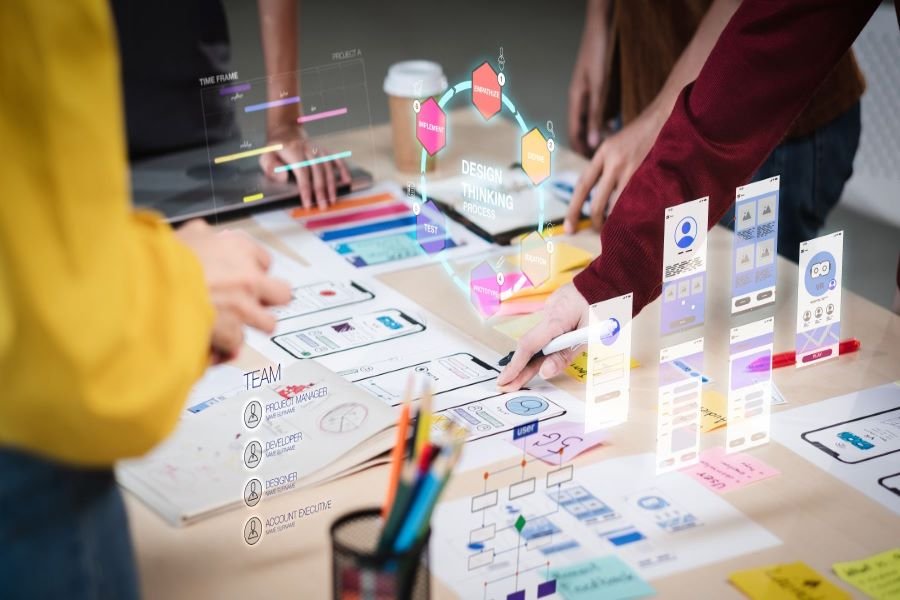

Interaction Design: Prototypes enable designers to visualize and test the interactive elements of a design, such as navigation, buttons, and animations. By prototyping interactions, designers can ensure a seamless and intuitive user experience, reducing the risk of usability issues. Interactions can be simulated in prototypes to validate their effectiveness, allowing designers to make necessary adjustments before final implementation. Testing the interactive aspects of the design helps refine the user flow, optimize navigation, and create engaging and intuitive interactions.
III. Collaboration and Communication:
Stakeholder Alignment: Prototypes serve as a powerful communication tool to align stakeholders and team members on the design direction. Visualizing the design concepts through prototypes helps stakeholders better understand the intended user experience and provide valuable input and feedback. Prototypes make it easier to convey design ideas, demonstrate functionality, and discuss potential improvements or modifications. This alignment among stakeholders ensures that the design meets business goals, user needs, and aligns with the overall project vision.
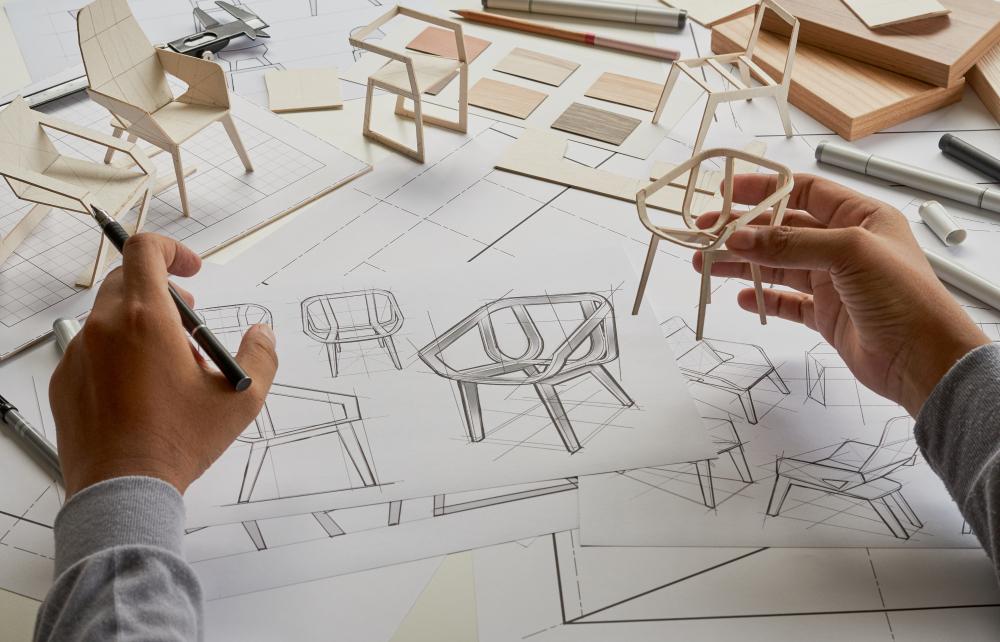

Collaboration: Prototypes encourage collaboration among designers, developers, and other stakeholders by providing a tangible representation of the design. Through prototypes, team members can actively participate in the design process, offering insights, suggestions, and solutions. Prototypes facilitate effective communication, idea sharing, and problem-solving, resulting in better design outcomes. Collaborative prototyping sessions allow for a collective understanding of the design, fostering a shared vision and fostering a sense of ownership and collaboration among team members.
In conclusion, prototyping plays a crucial role in the design process, enabling designers to validate design concepts, enhance the user experience, and foster collaboration and communication. By gathering user feedback, iteratively refining designs, and testing interactions, designers can create more successful and user-centric solutions.
Key Takeaways:
- Prototyping allows designers to gather user feedback and validate design concepts early in the process.
- Iterative design with prototypes helps refine designs based on user input and avoid costly mistakes.
- Prototyping enables testing and refining interactions to enhance the overall user experience.
- Prototypes facilitate stakeholder alignment and collaboration, fostering effective communication and idea sharing.
- Incorporating prototyping in the design process leads to more successful and user-centric design solutions.
We understand the importance of prototyping in delivering outstanding design outcomes. Contact us today to explore how we can leverage prototyping to bring your design vision to life and create meaningful experiences for your users.
Leave a Reply